Estonian pension system, how pensions are calculated
In Estonia, old age benefits are divided into stages:
- The first is minimal. Formed from funds transferred by the working population—33%.
- The second depends on the size of the salary. 2% is withheld from it plus 4% from social tax. Available to those born before 1982. Others could join until 2010.
Important information from BBQcash: news in 2020 - the project on a one-time payment of second pillar savings has been supported. They are not exempt from income tax, which will increase budget revenues.
- Third: optional or voluntary part. Private funds and insurance organizations provide an individual schedule and time of payments, amounts, suspension of payments, etc. Tax incentives available. Savings can be used from the age of 55.
For a normal life, a pensioner needs to have 65% of his available income. The first two steps give 40%, the rest is added by the third.
Features of pension calculation
The total amount of the pension consists of a basic amount of approximately 160 euros, a bonus for length of service until the end of 1998, as well as payments from the insurance share. The last component requires separate consideration, since there are a number of factors taken into account when calculating it.
Among them:
- compulsory service in the armed forces;
- work experience;
- availability of education;
- maternity leave or temporary disability;
- the amount of taxes paid before 1999.
Such insurance payments are calculated individually and differ significantly for each resident of Estonia. Each year of service increases the future pension by 5.7 euros, which must be taken into account when submitting documents.
There are special calculators for calculating the amount of contributions to a funded pension
It is worth remembering government measures designed to improve the well-being of local pensioners. Every year, authorities recalculate pensions, and pension payments increase. The size of the adjustment depends on the annual increase in prices, as well as the increase in social tax received by the state.
Watch the video: Pension system in Estonia.
Return to contents
Pension amount in Estonia
The amount of payments is calculated by adding up pensions:
- Basic – €191,649;
- Proportional - length of service until 1998;
- Insurance - years of payment of social tax since 1999.
The number of years is multiplied by the estimate. Now it is equal to €6,627. The pension is indexed annually in March by a coefficient depending on price increases and the social tax received. Since April 1, 2020, it has increased by 7%.
Minimum pension in Estonia
Minimum (or national) pension in Estonia: it is paid if the duration of work is insufficient. In 2020 - 205.21 euros.
Average pension in Estonia
The average pension is influenced by the employee's length of service. In 2020 - €483. The Estonian government has calculated the size of the increase:
- 2020 — €528;
- 2021 — €557;
- 2020 — €582;
- 2023 — €608.
The increase consists of annual indexation and a one-time increase.
Pension amount and retirement age
Today, about 315 thousand people have pensioner status in Estonia. However, there are several conditions that must be met to receive it, which is advisable to take into account when applying for benefits.
An old-age pension, or “national pension” as it is called in Estonia, can be assigned to citizens of the country or foreigners who legally resided in the territory of this state.
It is paid provided that the citizen’s work experience is less than 15 years, which means that it is not enough to receive a standard benefit.
The size of such a pension today reaches about 189 euros. At the same time, the maximum value of state payments can reach 375 euros, provided that the citizen has worked legally in Estonia for 44 years.
The retirement age in this country is set at 63 years for men and 62.5-63 years for women, depending on their date of birth. According to the government program for increasing this indicator, the retirement age will be gradually increased to 65 by 2026.
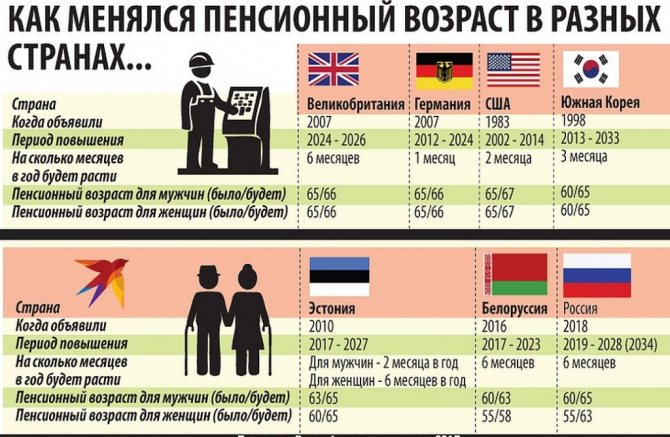
Changes in retirement age in different countries
Many native Estonians often go to work in neighboring European countries, where wages are significantly higher. This has led to a situation where more than half of the state's population are pensioners, while other citizens of the country work abroad.
You can also find out the salary level in Estonia on the website.
Return to contents
Types of payments for pensioners
Citizens can receive various types of pensions:
- State - for old age (15 years of experience required), disability, loss of source of income, early support (for those with only a minimum pension - 5 years after appointment).
- Folk - if there is not enough experience: reaching a set age and losing a breadwinner.
- Preferential - depends on the field of professional activity: harmful professions from lists No. 1 and 2, work in the police, judge, prosecutor and others.
Important information from BBQcash: every year of such work gives an increase of €5.7.
- For length of service - available when working in the police, rescue service, prison, civil aviation, mining or textile industry, navy, etc.
- In the event of the loss of a breadwinner - paid to family members with a certain length of service of the deceased. Applicants: children 18-24 years old, spouse or parents if they are pensioners or have limited ability to work.
- For incapacity for work - there is a conclusion about the inability to work. It can be full or partial - payments are prescribed if there is a loss of 40-100%.
Transfer of pension from Estonia to Russia

An agreement on cooperation in the field of pensions has been concluded between Estonia and Russia. Pensions in these two countries are calculated on the basis of length of service earned in their territory. When citizens move from one country to another, they are paid a pension by the country that calculated it.
By exchanging Estonia for Russia, pensioners lose the right to receive the national part of the pension paid to them in their former country of residence, but receive Russian benefits.
Such a move deprives pensioners of other additional pension benefits. For example, additional payments to the survivor's pension. When a pensioner moves from Estonia to Russia, his pension will be transferred to the account of one of the Estonian banks, which will transfer the amount received in euros into rubles.
As a result, the pensioner will lose part of his money during such a transfer due to exchange rate differences and bank interest for services provided.
Read a detailed article on how to transfer a pension from Russia to Germany.
Retirement age in Estonia in 2019
In 2020, people born in 1956 can apply for a pension.
Any Estonian citizen can receive a pension ahead of schedule, provided:
- layoffs;
- less than three years left until age;
- 15 years of work experience.
Upon employment, payments stop and resume again upon dismissal or reaching the required age.
Higher
Admission to Estonian universities is based on final testing, which school graduates take after finishing 12th grade.
The division of universities is carried out in the following way.
- Applied institutions.
- Universities.
The differences between them are the same as in Russia. The first category of institutions produces specialists in a specific field (for example, builders, doctors, etc.). The second has many unrelated faculties in which you can study at the same time.
A bachelor's degree at an Estonian university is awarded within 3 years from the date of admission.
The Master's degree requires 2 additional years of in-depth study of the industry.
Retirement age for women in Estonia in 2020 latest news
The factors determining the need for this procedure are based on a basis similar to the Russian economy - inflation, the intensity of which is reflected in the price tag for vital commodity items. Yet the process is somewhat different, since the increase occurs on a specific index, in which the price increase takes up only a fifth. The remaining share is determined by the dynamics of social tax.
The monthly pension in Estonia is set taking into account indexation at the beginning of April.
Average pension benefit for an Estonian citizen
The amount of old-age payments for the average Estonian is about 390 euros, which at the current exchange rate in rubles is 29 thousand.
Retirement age in 2020 in Estonia
Important
Due to this, the final benefit amount is significantly reduced.
Specifics of the third level of pension
Voluntary savings insurance is a service provided by many private funds and insurance organizations. It provides a number of features, it is advisable to study them in more detail. The main difference from government programs is the flexibility of conditions, which allows making the payment procedure as comfortable as possible for the client.
A person can regulate the amount and frequency of contributions made, terminate the agreement early, take advantage of the possibility of a payment holiday and many other nuances.
At the same time, a citizen will be able to receive the first payments from the fund at the age of 55.
An Estonian resident who decides to take advantage of such a program can count on tax benefits.
Each pension applicant has its own specific calculations.
Types of government benefits
If we consider the state part of the pension in more detail, it should be noted that there are several payment options that an Estonian citizen has the right to count on, subject to the occurrence of certain circumstances. Pensions paid by the state can be of the following types:
- For old age, subject to a mandatory work experience of 15 years.
- Due to disability. The amount of payments does not depend on length of service.
- Due to loss of source of income. Most often assigned to disabled citizens.
- Early retirement.
- Pension support.
The latter deserves special attention, since it is a serious help for low-income pensioners.
The state helps its citizens by paying 50% of the cost of keeping a child in a nursery.
In kindergarten, children do not have lessons, they are not graded. Teachers instill in children a love of animals and nature, help them discover their talents, and teach basic rules of etiquette. Communication takes place in Estonian.
Schools
Every citizen is required to receive secondary education. Training in such institutions is conditionally divided into 3 stages:
- introductory (from 1st to 3rd grade);
- general education (from 4th to 9th grade);
- narrowly focused (from 10 to 12 grades).
At the first stage, children learn to write and read through play. On the second, they become superficially familiar with the exact sciences and humanities. Having reached the third stage, the student selects several subjects in which he has a special interest.
Read also: Residence permit in Estonia for Russians Average salary in Estonia
Pensions
The Estonian pension system is divided into three parts:
- government provision (taxation of working residents and insurance policies);
- mandatory payment fund (2% of a citizen’s personal income + 4% from the state);
- additional benefits (determined on an individual basis).
Regarding the last point, this type of financial security is provided to a person upon reaching his 55th birthday.
Retirement age
An Estonian man has the right to retire at any time after reaching his 63rd birthday. For women the situation is more complicated:
- citizens born in 1951 or earlier can retire at 62;
- born from 1951 to 1953
When a pensioner moves from Estonia to Russia, his pension will be transferred to the account of one of the Estonian banks, which will transfer the amount received in euros into rubles.
As a result, the pensioner will lose part of his money during such a transfer due to exchange rate differences and bank interest for services provided.
How do pensioners live in Estonia?
The life of an Estonian pensioner is not as serene as it might seem. Most of them, after paying utility bills and buying medicine, have 1-2 euros per day left to live on. In order to understand whether this is a lot or a little for a state located in Northern Europe, you can compare this amount with food prices
The average price of bread in Estonia per kg is 1 euro.
Each year of service increases the future pension by 5.7 euros, which must be taken into account when submitting documents.
It is worth remembering government measures designed to improve the well-being of local pensioners. Every year, authorities recalculate pensions, and pension payments increase. The size of the adjustment depends on the annual increase in prices, as well as the increase in social tax received by the state.
Watch the video: Pension system in Estonia.
Receiving a pension in Estonia by citizens of the Russian Federation
Currently, the benefit for Russian citizens living in Estonia is 312 euros.
Attention
The social tax rate in Estonia is 20%. The remaining two parts of the system include the mandatory and supplementary pension funds.
The sources of their formation are the personal funds of the future pensioner. When a citizen of the country transfers 2% of his income to the mandatory pension fund, the state adds 4% from his social tax. The amount of contributions to the additional pension fund is determined by citizens independently.
Amount of monthly cash benefit
Those who have reached retirement age are paid an old-age pension or a national pension. The right to receive a state pension accrues to citizens of the country and foreigners who have permanent residence there if they have work experience earned in Estonia.
Source: https://pravo60.ru/pensionnyj-vozrast-v-estonii-v-2019-godu
Pension system
A pension is a payment in the event of old age or disability, as well as in the event of the loss of a breadwinner. The purpose of a pension system is to provide a monthly income to a person who has retired.
1st stage
First stage payments constitute the minimum subsistence level. State pensions depend on the amount of taxes that come from the payments of the working population. As is the case throughout the world, the number of working-age people is becoming smaller and smaller.
2nd stage
Payments from this stage are made up of personal contributions, from which 2% is withheld monthly. The state adds its 4% to this percentage. And the result is 6%, which a person receives while retired. The greater the salary a citizen receives, the greater the deductions, the greater the future payments.
Being in the second stage is mandatory for those born after 1982. If a person, having reached the age of 18, could not independently decide which fund his income deductions will go to, then the state itself will take care of this. The choice is made by drawing lots.
3rd stage
Here a person independently decides on the amount of deductions. For normal existence, future payments should be 65% of income. The first two levels will give 40%, and the remaining % will be collected by the future pensioner himself.
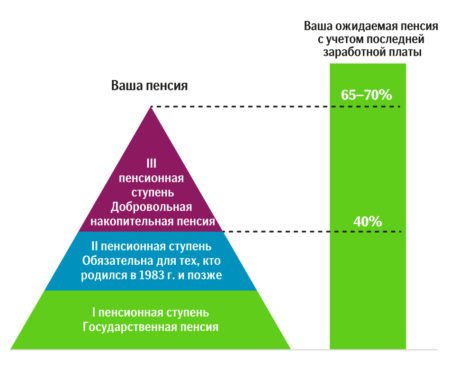
The total amount of the benefit is calculated as the base amount (160 euros), bonuses for the length of service worked before 01/01/1999 and the amount of the insurance share. Each pension applicant has its own specific calculations.
How do they live in Estonia?

Prices
Life in the Baltic state is slightly more expensive than in Russia and Ukraine. The average bill in a cafe for two here is 8-10 euros, in a restaurant – 15-25 euros. A one-way trip on public transport costs 1.5 euros, the same price as a liter of gasoline. Prices for products in Tallinn supermarkets:
| Name | EUR |
| Water (0.5 l) | 0,7 |
| Beer (0.5 l) | 1,5 |
| Imported alcohol (0.75 l) | 5-6 |
| Carbonated drinks (0.5 l) | 0,9-1 |
| Cereals (1 kg) | 1,4 |
| Milk (1 l) | 0,8 |
| Tomatoes | 2,2 |
| Bakery products | 0,3-0,6 |
| Bananas | 1,16 |
| Oranges | 1,3 |
| Apples | 1,3 |
| Potato | 0,38 |
| Meat | 5-6 |
| Cheeses | 6-7 |
| A dozen eggs | 1,3 |
| Chocolate bar | 0,5 |
| Chocolate bar | 1 |
Local residents recommend tourists buy groceries in stores and cook their own food, since daily visits to coffee shops and restaurants are very expensive even with a well-planned budget.
Pensions
The Estonian pension system is divided into three parts:
- government provision (taxation of working residents and insurance policies);
- mandatory payment fund (2% of a citizen’s personal income + 4% from the state);
- additional benefits (determined on an individual basis).
Regarding the last point, this type of financial security is provided to a person upon reaching his 55th birthday.
Retirement age
An Estonian man has the right to retire at any time after reaching his 63rd birthday. For women the situation is more complicated:
- citizens born in 1951 or earlier can retire at 62;
- born from 1951 to 1953 – at 62.5 years;
- the rest - from 63 years old.
The reason for this inconvenient calculation is legislative innovations. The 2020 reform states that women born between 1954 and 1960 have the right to retire from age 63. In the future, the age limit will be even higher.
Size

The average amount of state payments to elderly Estonians is 391 euros (approximately 24,027 rubles). Retirement in 2020 is affected by the length of service, the citizen’s income, his state of health, as well as participation in various government programs. If a person has officially worked for 15 years, he will receive a pension of 223 euros or more, 30 years - 300 euros, 40 years - 354 euros, more - 375 euros. In 2020, the amount of government payments in Estonia will be higher by 5.7%.
Taxation
The Estonian tax system is unique - it does not impose income penalties on legal entities. Formally they exist, but the size is 0%.
List of taxes in 2020:
- turnover (VAT) – 20%;
- social rate – 33%;
- dividends – 20 to 80%;
- on unemployment - workers pay 1.6% of income, and company owners - 0.8%;
A similar system applies to individuals. If a person does not sell goods and services within the state, VAT is 0%. For those who head a company, but cooperate with a non-resident (without an official structure), in this case the company’s profit is also not subject to taxation.
Lifespan
The stereotype that people living in villages have a chance of “making it” until their hundredth anniversary is not true. In Estonia, there are more centenarians among the urban population, since salaries in megacities are much higher and medicine is more advanced. Between 2009 and 2020, the average life expectancy for men was 59 years, for women – 54-56 years.






