Pensions, regardless of their type, are not subject to income tax in 2020.
Personal income tax is withheld from employers' contributions to an employee's funded pension, from additional payments to pensions not provided for by law, from the wages of working pensioners, from investment income, and savings upon termination of an agreement with a non-state pension fund.
A pensioner can take advantage of the social tax deduction only from amounts transferred personally to a non-state fund, but upon termination of the contract, it is deducted from the redemption amount.
Russians are required to pay personal income tax on any income. But a pension, in essence, is a return of contributions from working citizens or social state security.
Can such payments be classified as income, which is the basis for withholding income tax and entitles pensioners to take advantage of a tax deduction? It all depends on the type of payments and other conditions for the formation of pension provision.
Therefore, we will understand in what cases a pension is subject to income tax in 2020.
Income tax on pensions
Income of citizens of the Russian Federation and non-residents received from Russian or foreign companies through separate divisions on the territory of Russia, in cash or in kind, in accordance with Art. 208 of the Tax Code, are subject to income tax at a rate of 9 to 35%. Cases expressly excluded by law from the tax base are not subject to taxation.
Therefore, the statement that pensions are not subject to personal income tax is not entirely correct. Tax is not withheld only from payments specified in the list of exceptions reflected in Art. 217 NK.
The following types of payments to pensioners are not subject to taxation:
- State pensions, including:
- long service payments to state and municipal employees;
- maintenance paid to pilots, cosmonauts, and retired military personnel;
- provision of support for persons affected by or liquidating the Chernobyl accident;
- old age social benefits;
- social benefits for disabled people in old age;
- survivor's insurance.
- Insurance pensions, including:
- calculated part of the labor pension;
- a fixed payment added to the insurance coverage;
- early pension provision;
- disability payments;
- survivor payments.
- A funded pension established by law.
It turns out that all main types of pension payments are excluded from the taxable list, therefore income tax is not withheld from payments that pensioners receive in old age from the pension or state budget.
Are pension supplements taxable?
If the main types of pensions are “untouchable” for tax, does the veto apply to additional payments, allowances and indexation?
Rice. 1. Federal and regional pension supplements are not taxed
The law states that any social supplements to pensions paid in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation and the constituent entities of the Russian Federation are exempt from taxation.
It turns out that additional payments up to the minimum subsistence level of a pensioner, both federal and regional, are not subject to income tax. This norm remains the same even in cases where the amount of the social supplement exceeds the amount of the pension itself.
The category of preferential benefits includes additional payments to WWII veterans, residents of besieged Leningrad and regional allowances to labor veterans.
Other types of increases provided for by law also cannot be taxed. These preferential additional payments include:
- increasing the fixed payment for dependents;
- double fixed payment to pensioners after 80 years of age;
- preferential additional payment to the PV if you have northern experience and production in regions equated to RKS.
The list of exceptions also includes all coefficients that increase payments for pensioners:
- motivating;
- regional;
- provided for the small peoples of the North.
Indexation, as well as the growth of payments tied to cash support, do not relate to additional income, but are a method of recalculating pension provision in accordance with the level of inflation, the minimum wage and other social indicators. Therefore, such increases in payments to pensioners are not the basis for withholding personal income tax.
However, pension increases that are not provided for by federal or regional legislation, from the point of view of tax legislation, are generally considered additional income. This is the explanation given by the Ministry of Finance:
- Letter No. 03-04-05/48965 dated July 13, 2020 states that corporate pension contributions at the expense of the employer are not exempt from income tax. Regardless of whether such a bonus is paid to a working retiree or a former employee, it will be taxed at a rate of 13%.
- Letter No. 03-04-06/46210 dated October 30, 2013 states that monthly supplements to the labor pension of municipal employees, by decision of the local government, are not included in the list of preferential benefits under Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, such payments are subject to taxation as income of individuals.
If, upon retirement, the employer pays a pensioner severance pay, tax will be calculated on an amount not exceeding 3 times his average monthly salary.
For workers in the northern regions, the benefit applies to amounts exceeding 6 times their salary. This rule has been in effect since 2012.
, as explained by the Federal Tax Service in letter No. AC-4-3/ [email protected] dated September 13, 2012.
Personal income tax on the income of working pensioners
Working pensioners belong to a special group, as they receive payments from different sources.

Rice. 2. Standard taxes are withheld from pensioners’ salaries.
But their income is not always subject to taxes:
- state or insurance pensions are exempt from taxation;
- basic salary is subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%;
- bonuses and additional pension incentive payments transferred by the employer are considered additional income and are subject to income tax.
Note! Personal income tax is withheld from any additional income of a pensioner other than a pension or social benefit, including from investment or business activities or receipt of dividends.
Income tax on “non-state pension”
The provisions set out in Art. 217 of the Tax Code do not fully disclose the features of taxation of funded pensions. The regulation states that this type of security does not relate to income, but only if it is state-owned.
It turns out that payment of savings accumulated in the period from 2004 to 2014, when contributions to the Pension Fund were divided into insurance and savings, cannot be subject to income tax.
This requirement remains the same when transferring savings to non-state entities.
After all, in fact, savings are part of the salary on which personal income tax is already paid, deferred for old age and transferred to the management of a state or non-state structure.

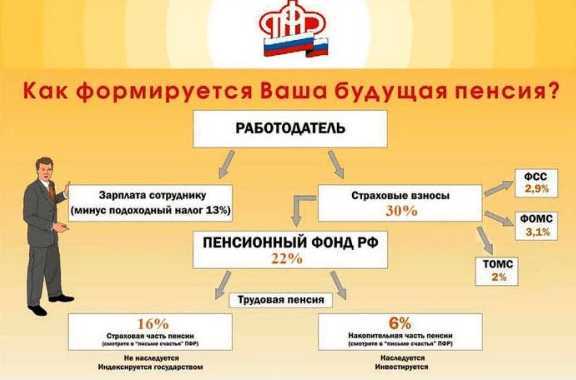
Rice. 3. Non-state pension provision is a guarantee of stability in old age
But the alternative pension program did not cease to exist due to the introduction of a moratorium on funded pensions. To generate additional income in old age, non-state support programs are provided.
From the point of view of personal income tax withholding, the law considers such payments in terms of the source of financing:
- If contributions are paid by an individual for himself or a third party: parents, children, brothers, sisters, grandchildren, grandparents, payments are not the basis for withholding income tax, since they are made from income that has already been taken into account when calculating personal income tax.
- When funding is provided through corporate programs, where the employer makes contributions for the employee, the payments are subject to taxation. In this case, the tax is paid by the NPF, that is, the amount minus income tax is credited to the client’s personal savings account.
Is the pension subject to income tax (nuances)?
To which pension fund is it better to transfer the funded part of the pension? Is the pension subject to income tax? Such questions arise when a pensioner decides to take advantage of personal income tax deductions provided for by tax legislation. After all, if a pensioner does not have taxable income, then he has nothing to reimburse the tax from.
Income tax on pensions
Income tax refund for pensioners
Where is it more profitable to transfer the funded part of the pension?
Results
Income tax on pensions
In accordance with clause 1.7 of Art. 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, pensions are recognized as income received from Russian sources through payments from Russian organizations or outside of it from a foreign company through a separate division in the Russian Federation. And income is subject to taxation at a rate of 13% (clause 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To understand the question of whether your pension is subject to personal income tax, you need to consider the following:
- State pensions, according to clause 2 of Art. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not subject to personal income tax, with the exception of payments if the individual has voluntary insurance of the funded part of the pension.
- Non-state pensions are subject to personal income tax due to the provisions of clause 2 of Art. 213.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (with the exception of payments provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 213.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be noted that pensions in the Russian Federation can be accumulated either in a state pension fund (including under voluntary insurance contracts for the funded part of a pension) or in a non-state one. The effect of state pension provision is regulated by the laws “On State Pension Security” dated December 15, 2001 No. 166-FZ and “On Insurance Pensions” dated December 28, 2013 No. 400-FZ.
Non-state pension provision is carried out in accordance with the Law “On Non-State Pension Funds” dated 05/07/1998 No. 75-FZ.
Within the framework of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the procedure for taxation of pensions formed by transferring contributions to state or non-state funds has different specifics.
Thus, non-state pensions are subject to personal income tax.
Find out what your pension will be if you have no work experience from this publication.
Income tax refund for pensioners
A pensioner can return income tax in the following cases:
- The pensioner works and receives taxable income.
- The pensioner worked for the last three years, which preceded the period when the deduction arose, and received income that he can transfer (paragraph 4, paragraph 3, article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 10, article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Mandatory pension contributions were transferred to a non-state pension fund or voluntary contributions were transferred.
This article will tell you about the nuances of calculating pensions.
Where is it more profitable to transfer the funded part of the pension?
After the introduction of the moratorium in 2014, many began to wonder whether it was worth transferring the funded part of the pension - the part that had been accumulated before the ban on payment was introduced. The answer is simple: if you do not want to lose on the profitability of your pension savings, then it is better to transfer the funded part of your pension to 2018-2019, because the moratorium has been extended.
Is it possible to transfer the funded part of the pension? Yes, this is not prohibited and is highly desirable, since by default the funded part will be transferred to the insurance part and, naturally, no increase in profitability should be expected.
Where can I transfer the funded part of my pension? To any non-state pension fund (hereinafter referred to as NPF). The future pensioner will only need to choose where it is best to transfer the funded part of the pension. It is highly advisable to opt for a non-state pension fund that is part of the guarantee system and has several management companies.
How to transfer the funded part of the pension? It is necessary to submit the appropriate transfer applications to the selected NPF and the Pension Fund.
Results
All pensions that retirees receive are income. However, state pensions are not subject to personal income tax, and only pensions, payments of which are made by non-state funds, are subject to taxation. Thus, if a non-working pensioner decides to take advantage, for example, of a property deduction for personal income tax, he will be able to do this if, before the right to the deduction arose, he received taxable income during the three previous years or receives a non-state pension.
Subscribe to our accounting channel Yandex.Zen
Subscribe
nalog-nalog.ru
Income tax on pensions of working pensioners
Currently, there are a number of programs operating at the state level, within the framework of which financial and social assistance is provided to pensioners. In addition, current legislation provides for preferential conditions for taxation of pensioner income. In this article we will look at whether it is necessary to withhold personal income tax from a pensioner’s salary.
What pensioner income is subject to personal income tax?
According to the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income subject to personal income tax includes wages and other payments received by a citizen on the basis of an employment contract or a civil law agreement. In addition, a citizen is obliged to pay personal income tax provided that the income is received in the following cases:
- winning the lottery;
- Property For Sale;
- sale of movable property;
- receiving ownership of property under a gift agreement;
- dividends from investments;
- payment of pension savings from non-state pension funds.
A pensioner who has received income on one or more of the listed grounds is recognized as a personal income tax payer in the general manner.
Is it necessary to withhold personal income tax from a pensioner’s salary?
An employer performing the functions of a tax agent is obliged to calculate, withhold and transfer to the budget in accordance with the deadlines and procedures provided for by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When calculating personal income tax for a retired employee, the employer should take into account the standard rate of 13% in the general procedure, or the rate of 30% if the employee of the enterprise is a non-resident of the Russian Federation.
| ★ Best-selling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8,000 books purchased |
Deadline for payment of personal income tax from the salary of a retired employee
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the deadline for paying personal income tax is determined by the day following the day of payment of taxable income to the employee in the form of salary. This rule applies to the payment of personal income tax withheld from the income of a pensioner.
As a rule, employers transfer personal income tax to the budget on the day the employee’s salary is paid, or the next day, but not later. If the company paid wages to employees on Friday or on a pre-holiday (the next day is a day off), then the deadline for transferring personal income tax is the first working day following the weekend/holiday.
When paying temporary disability benefits and vacation pay to a retired employee, the period for transferring personal income tax is determined as the last day of the month in which the company made transfers in favor of the employee. In accordance with these deadlines, personal income tax withheld from income in kind must also be paid.
Deductions when calculating the personal income tax of a retired employee
Current legislation does not provide for the use of tax deductions based on retirement age or in connection with an employee receiving an old-age pension. At the same time, a retired employee has the right to apply for the following types of deductions in the general manner:
- for children (1,400 rubles each for the first and second children, 3,000 rubles each for the third and subsequent children);
- for a disabled child of groups I and II under 18 years old – 12,000 rubles;
- for treatment - in the amount of actual expenses incurred, supported by documents (no more than 120,000 rubles/year);
- for training - in the amount of expenses actually incurred, confirmed by documents (up to 120,000 rubles/year - for your own training; up to 50,000 rubles/year - for training relatives);
- when purchasing a home – in the amount of the cost of the home, but not more than 2,000,000 rubles;
Source: https://upbizn.ru/podohodnyj-nalog-s-pensii-rabotayushhih-pensionerov/
Is income tax taken from pensions and EDV in Russia?
Most of the income of citizens in the Russian Federation is subject to personal income tax. Tax is withheld from wages, income from business activities, and other receipts and payments. But some accruals in favor of Russians are not subject to taxation. We are talking about pensions, compensation and one-time cash payments, although some exceptions are assumed here.
Personal income tax from pensions
The provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2, article 217) indicate that state pensions and compulsory pension benefits, including fixed, insurance and funded payments, are not subject to income tax. Similar conditions apply to social supplements to pensions.
However, personal income tax withholding is still allowed for some types of pensions. These include:
- Pension payments at the expense of non-state pension funds. The provision is valid provided that the agreement with a non-state fund was concluded on behalf of the employer of the insured person (future pensioner). In this case, the part of the pension paid from additional sources from non-state funds is subject to income tax. The situation is different when an agreement with a non-state pension fund is concluded directly by the citizen himself, who transfers regular contributions. In such situations, income tax will not be withheld when paying pensions.
- Pension payments from NPF funds are subject to personal income tax if an agreement is concluded between the fund and an individual, but in favor of third parties.
Is the pension subject to personal income tax?

Financial payments to pensioners occur regularly. Usually monthly. It should be noted that a pension can be assigned not only for length of service, but also for loss of ability to work, disability, loss of a breadwinner, and military pensions. That is, the circle of people in our country is much wider than we imagine when we hear the word “pensioner”.
The Russian Federation has established the obligation to pay tax on amounts of income received. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes four percentage rates for such a tax: 9%, 13%, 30%, 35%. The basic rate is 13%.
Does this mean that pension payments are also taxed at 13%? Yes, but not always.
In order to find out whether tax will be charged on a pension, you need to determine which category this payment belongs to. It depends on the source of funds:
- Public : Money paid out of public pension funds is not subject to income tax. This happens because the payment is made taking into account the tax. This rule is contained in Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Non-state . If citizens choose a fund that does not belong to the state as a source of payment of pension amounts, then a tax of 13% will be required on such payments. This is a requirement of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 2 of Art. 213.1.
This means that income tax on pensions in Russia is paid if the funds are placed in a non-governmental organization or in a state organization, but under a voluntary insurance agreement.
Income tax on pensions in Russia: in what cases is it withheld?
Many individuals are interested in the question of whether income tax is removed from pensions in Russia. In this regard, we propose to talk in this article about the procedure for paying personal income tax from pensions, and also consider all the nuances that affect this kind of procedure.
Personal income tax on pension payments
Various material payments, provided to individuals not only for length of service, but also for disability, as well as in the absence of work ability, are called pensions.
As a rule, payments of this kind are received by pensioners from the state budget and are provided systematically (usually once a month). The size of pensions is not the same for all citizens of the Russian Federation and depends on many factors - the reason for accrual, age and position in which the individual worked, health status, as well as some other circumstances.
It should be noted that if a family has lost its breadwinner, as a result of which minor children are left without financial support, then by law the state is obliged to provide them with compensatory pension benefits and pay them regularly.
What the law says
If you turn for help to article number 224, which is an integral part of the Tax Code of Russia, it becomes clear that this type of social payments, such as pension benefits, is not always subject to income tax withholding. The tax rate for personal income tax is not one, but four (9, 13, 30 and 35%). As for pensions, thirteen percent is deducted from them to pay taxes, but not in all cases.
In order to figure out whether it is worth paying thirteen percent of pensions, it is necessary to determine what type of body is the one providing these benefits. Pensioners can receive such social compensation payments from two types of sources:
- State - if money for individuals comes from state pension funds, then there is no need to return 13% back, since the amount of the payment is already initially calculated taking into account the tax (the fact that personal income tax is not withheld from state pension benefits is recorded in the second paragraph Article No. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Non-state - if pensioners receive money with the help of organizations that do not belong to the state, then they are required to pay income tax. This fact is evidenced in the second paragraph of Article No. 213.1.
Exceptions to the General Rules
However, in some situations, taxes must be paid even on pensions paid by government-type funds. We are talking about the funded part of pension benefits that individuals have as a result of taking out insurance on a voluntary basis.
That is, the part of the labor pension formed as a result of pension savings separately recorded in an individual personal bank account, the owner of which is the insured individual, is taxed. Otherwise, the pensioner will bear tax liability.
As for payments, the sources of which are non-state enterprises, here too there are several exceptions that give taxpayers the right not to pay personal income tax to the state treasury:
- Cumulative benefits - if an individual receives any material funds coming to him from a funded pension benefit, then they should not be taken into account when determining the size of the tax base.
- If the fund has a license, those pensioners who have entered into an agreement with non-state organizations licensed to provide appropriate cash benefits are not required to transfer personal income tax to the state budget system from the compensation received.
- If the agreement is concluded by the employer, in some situations, company managers use the services of licensed non-state pension funds. In the case of drawing up agreements of this kind, retired employees of companies who in the past worked for the manager who initiated the conclusion of such an agreement do not have to pay taxes.
- If the agreement was not drawn up by the pensioner himself, often close relatives of individuals come to non-state funds, check whether this organization has a license, and then sign an agreement on providing a pension, but not in their favor. After this, subject to all the conditions specified in the agreement, the compensation benefit that will be received by the individual recorded in the document as a third party will not be subject to personal income tax.
Is it possible to return tax paid on pensions?
Russian legislation provides for a number of cases that give the right to an individual who has previously paid income tax on pension benefits to reimburse these material assets, which include the following:
- Personal income tax is deducted from profits. Most individuals both work and receive pension benefits, since combining these two concepts is not prohibited by law. In such situations, pensioners may be accrued benefits with personal income tax deducted, which they as a result have the right to return.
- The pensioner worked during the period when the right to the deduction arose. Also, those individuals who performed their official duties during the last three years that elapsed before the start of the deduction period and, most importantly, received income subject to personal income tax, can also refund the income tax from their pensions.
- Benefits were transferred to a non-governmental organization. Often, pension payments are first transferred to a state-type fund, and only then go into the hands of individuals to whom they are entitled by law. If circumstances of this kind occur, the previously withheld tax will be compensated.
Who will pay this tax and when?

All employees of public sector activities, those who have social benefits from the state, accept government payments, and pensioners have been transferred to the new Russian payment system MIR since 2018. The joint stock company “National Payment Card System” officially appeared in July 2014. But development began back in 2011. Before the payment system appeared on the market, providing money transfer and storage services, it had fully established its operation, taking into account the latest technical developments. First of all, this system meets international quality standards for making secure payments. What are the features of a plastic card?
- The name and logo are the result of an all-Russian vote.
- A hologram is a special square sign that allows you to distinguish a fake from a real card.
- Hidden signs. For example, when scanning a card with ultraviolet light, a currency symbol appears: ruble.
- A distinctive sign of the WORLD card is the application of a pattern.
The pension tax in Russia in 2020 began its work from the beginning of the year. All state employees received new cards in the first half (before July 1), and new clients - from July 1. But after the decree is issued, all pensioners do not need to immediately run to the bank to change their card. Each of them has a certain validity period. As soon as it ends, the card holder needs to come to the branch of the servicing bank. There he will receive a new card from the MIR payment system.
Pensions and insurance compensations | Tax and Customs Board
resident individual may, on the basis of Part 1 of Article 281 of the Income Tax Law, deduct from his income the mandatory funded pension payments withheld and paid during the tax period.
The payment rate for the mandatory funded pension in 2014–2017 was 2% or 3% . The presence of an obligation to withhold payment for a mandatory funded pension and the applicable payment rate in 2014–2017 for a specific individual can be checked by personal code or by mass request.
Since 2018, the payment rate for compulsory funded pensions for all obligated persons is 2%.
Income tax on pensions paid to Russian residents in Estonia
Individuals who live in Russia are considered non-residents within the meaning of the Income Tax Law, and when paying them a pension in Estonia, income tax is withheld at a rate of 20% .
The income tax withheld upon payment is final. This means that a non-resident living in Russia and receiving a pension from the Social Insurance Department in Estonia, on which income tax is withheld, does not have the right to submit an income tax return in Estonia for a resident individual to make deductions from taxable income.
In Estonia, income tax withheld from payments made to a pensioner living in Russia is not refundable.
Tax changes when taxing additional funded pensions
Since 2013, it has become possible to move funds between voluntary pension funds and the pension insurance system without interrupting the five-year period for applying the 10% tax rate for a person who has reached 55 years of age and joined the supplementary pension insurance system.
Until now, the return value under the insurance contract for an additional funded pension could not be contributed to the voluntary pension fund without interrupting the five-year period, but according to the changes, the five-year period is counted from the earliest date, i.e.
from the date of conclusion of the insurance contract. It is also possible in the future to transfer the cost of redemption of pension fund shares when concluding an insurance contract without interrupting the five-year requirement.
The five-year period will be calculated from the date of the initial acquisition of shares of the voluntary pension fund, if it was earlier than the date of conclusion of the additional funded pension insurance agreement.
The period is counted from an earlier date or from the date of concluding an additional funded pension insurance contract, or from the date of the initial acquisition of shares of a voluntary pension fund.
The contribution to the transfer of the reserve fund cannot be deducted from income for tax purposes, since the person already had the right to receive a tax benefit from this part.
What taxes do working pensioners pay?
In the Russian Federation, many people work informally after retiring, since it is very difficult to live on payments alone. That's why they have to pay tax. In our country, only those who have benefits or are deprived of property do not pay them. However, the status of a working pensioner has its advantages:
- receiving tax deductions;
- use of benefits;
- the opportunity not to pay contributions on any property.
Everything else is taxed in the same way as for other citizens who are not pensioners.
Many pensioners take advantage of the opportunity to receive benefits from the state. For example, federal beneficiaries have some advantages. This category includes war veterans, disabled people, former military personnel, Chernobyl victims, etc. All regions of the country provide benefits for these citizens. They do not pay transport, property or land taxes.
If we talk about income tax, it is levied in full on winnings, dividends and other income. In such a situation, pensioners are no different from other citizens. If you pay your taxes on time, you may be entitled to a refund of a portion of the following costs:
- For treatment and medical services – 40-50 thousand rubles.
- For the purchase of housing - 2 million rubles.
- To pay interest - 3 million rubles.
- For the sale of property - 1 million rubles.